A Price Floor Set Below The Equilibrium Price Leads To

Taxation and dead weight loss.
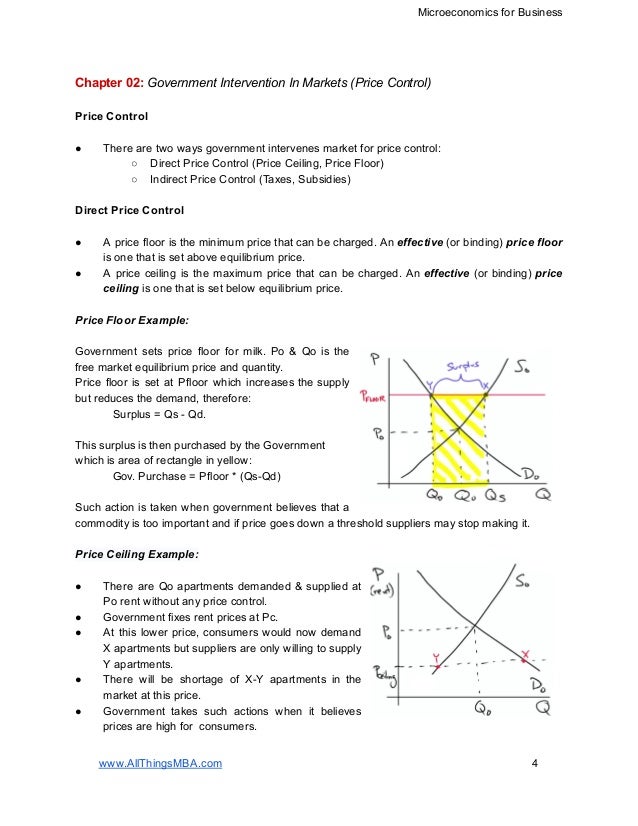
A price floor set below the equilibrium price leads to. When they are set above the market price then there is a possibility that there will be an excess supply or a surplus. Price floors are only an issue when they are set above the equilibrium price since they have no effect if they are set below market clearing price. Price ceiling a price ceiling is a government set price below market equilibrium price. Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences.
Minimum wage and price floors. How price controls reallocate surplus. A binding price ceiling leads to a n. Price and quantity controls.
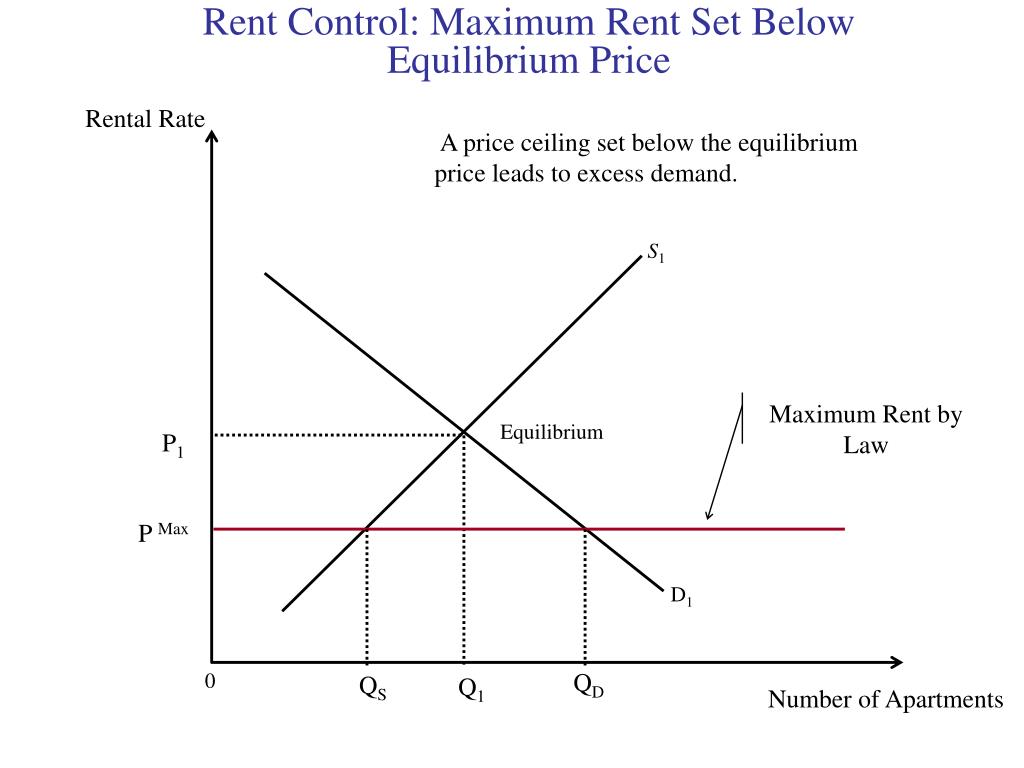
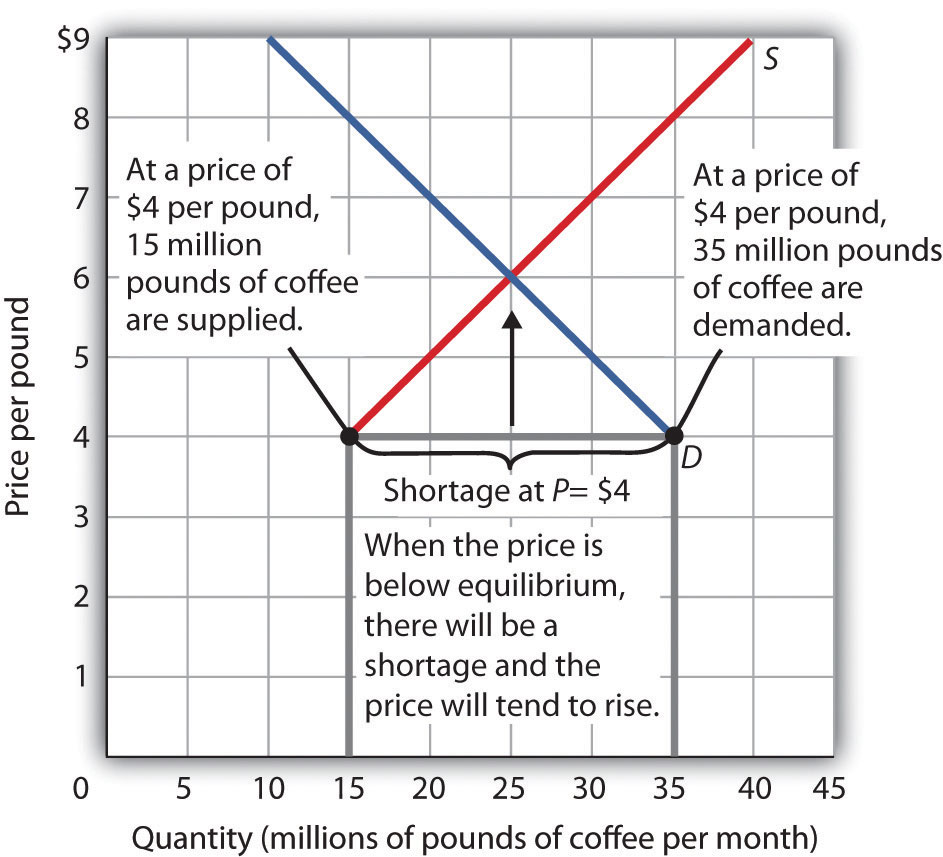
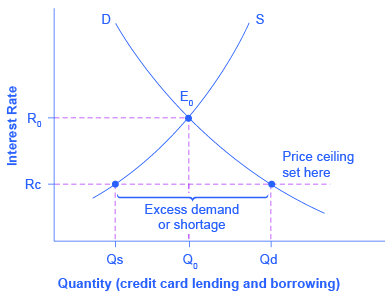
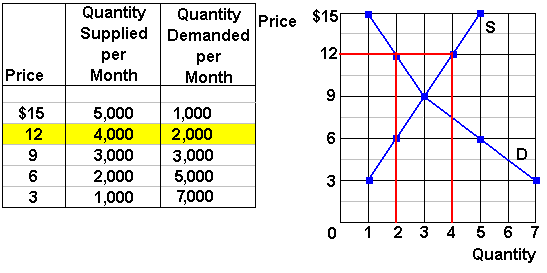
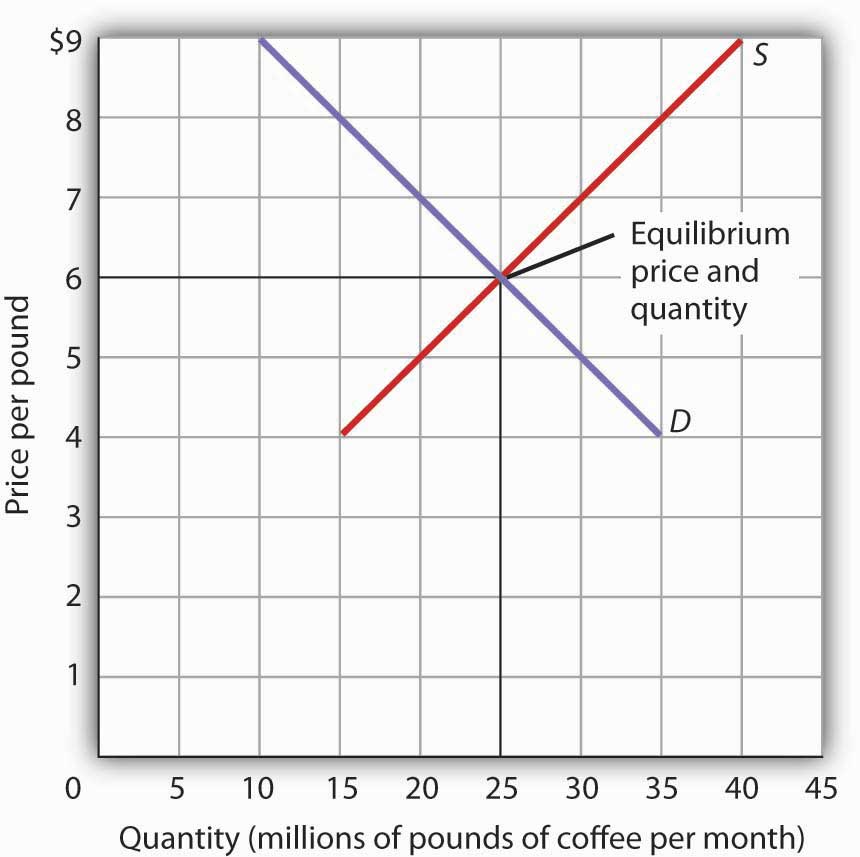
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external. It is an implicit tax on producers and an implicit subsidy to consumers. When a price ceiling is set a shortage occurs. The result is that the quantity supplied qs far exceeds the quantity demanded qd which leads to a surplus of the product in the market.
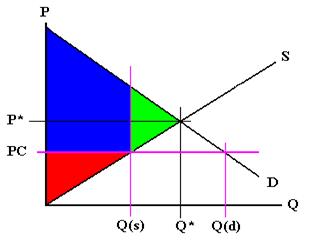
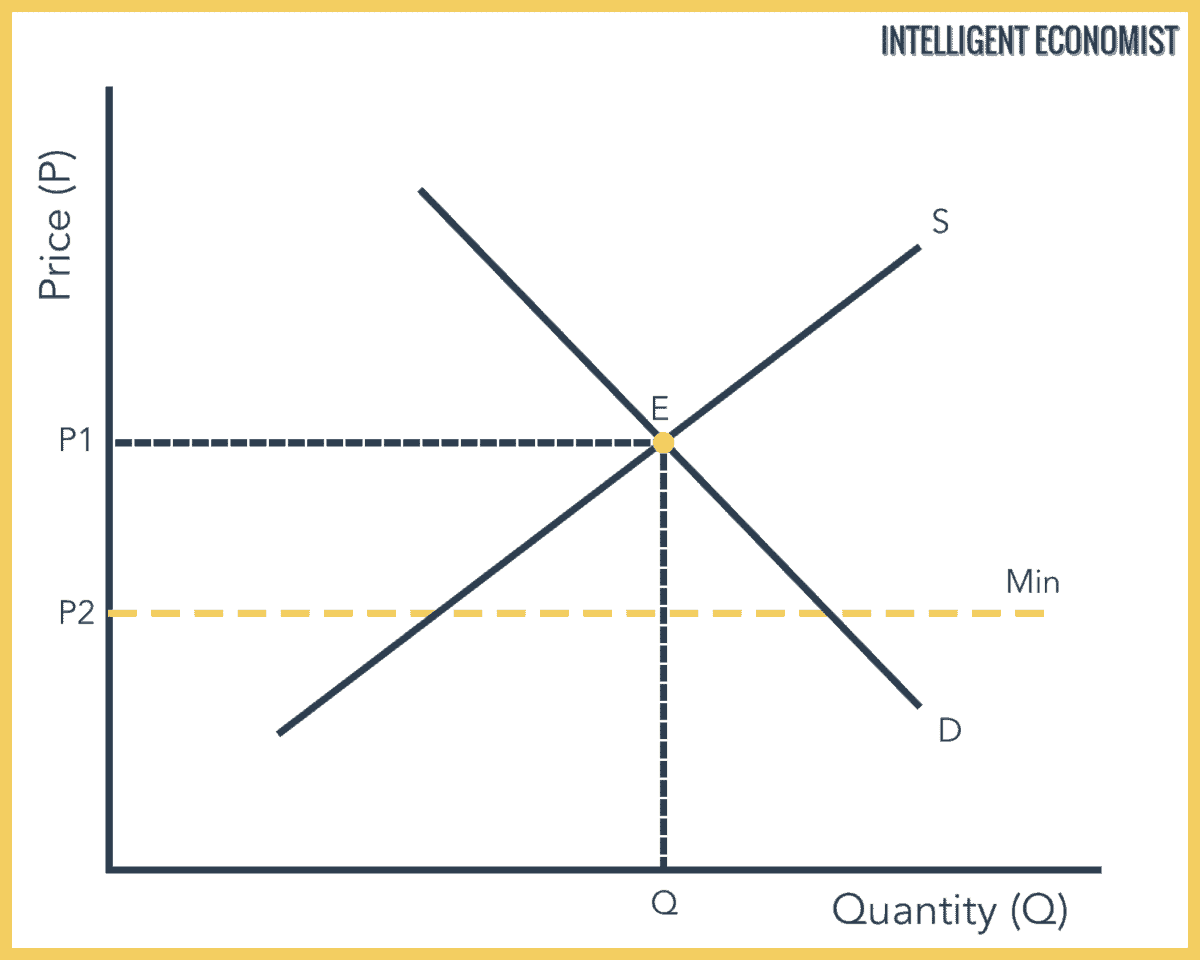
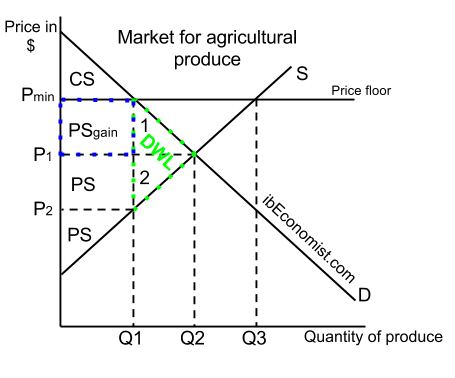
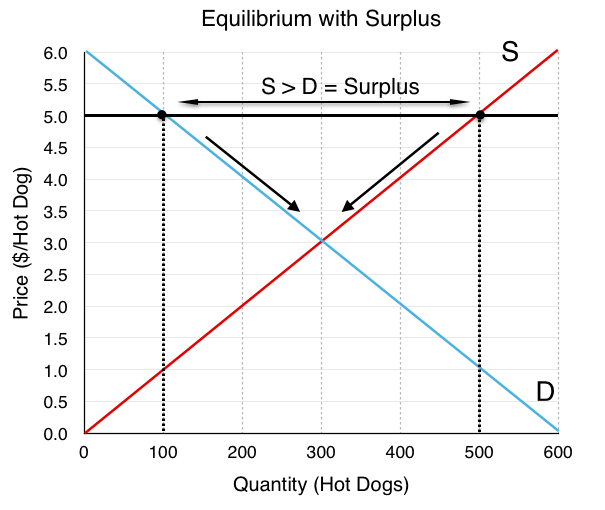
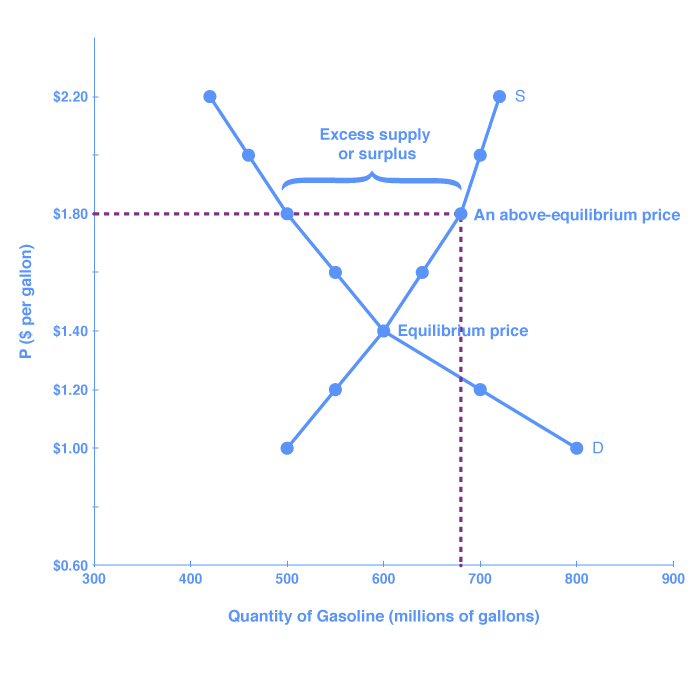
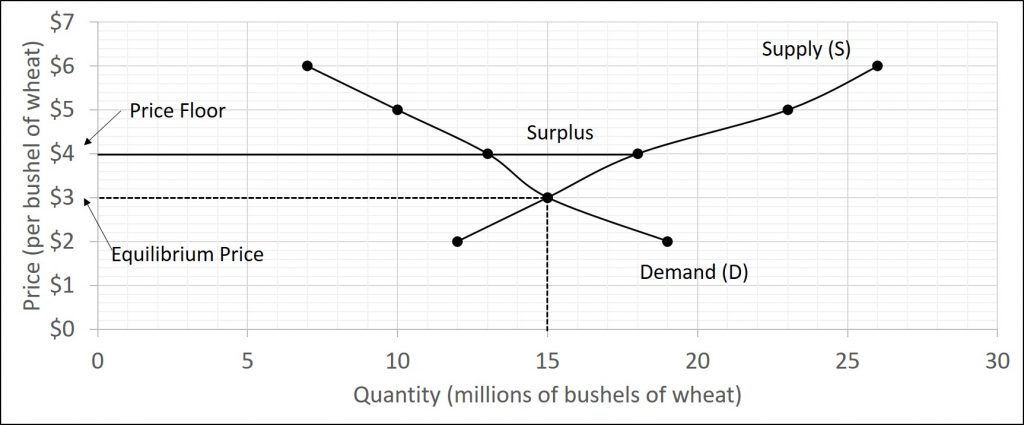
This is the currently selected item. A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective. The result is a quantity supplied in excess of the quantity demanded qd. When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.
Price floors cause surpluses. In order for a price ceiling to be effective it must be set below the natural market equilibrium. B quantity of zero units. The effect of government interventions on surplus.
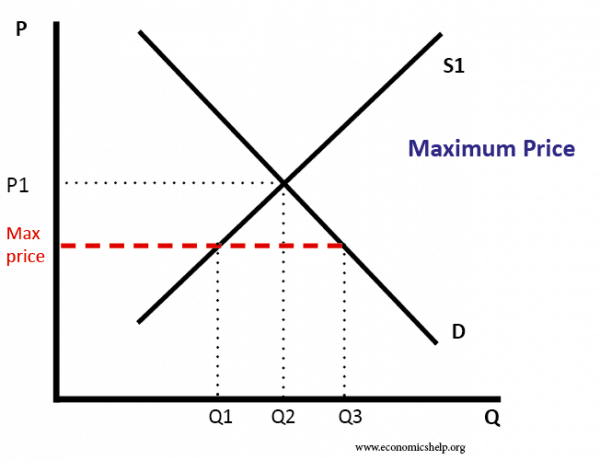
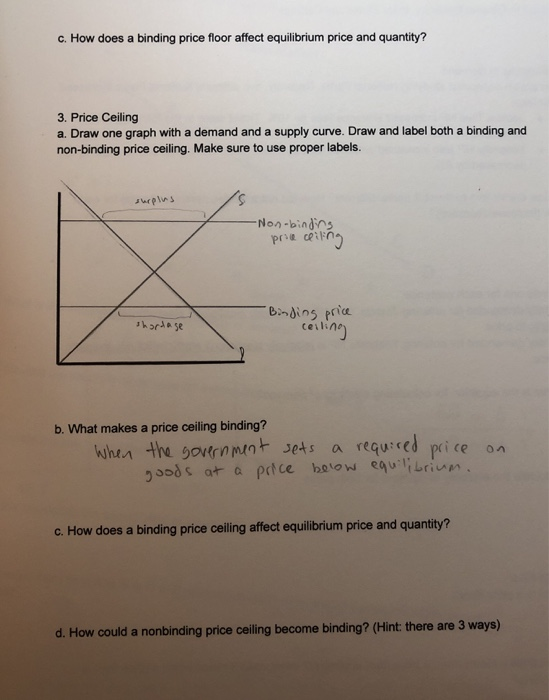
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level. If set below the equilibrium price it would have no effect. A price ceiling occurs when the government puts a legal limit on how high the price of a product can be. As seen in the diagram minimum price is set above the market equilibrium price.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service. When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded a surplus exists. Example breaking down tax incidence. When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price as in this example it is considered a binding price floor.
In the price floor graph below the government establishes the price floor at price pmin which is above the market equilibrium. Do these create shortages or surpluses.




















/disequilibrium-498e9ba4154c4a7c8739b3443da14b17.png)