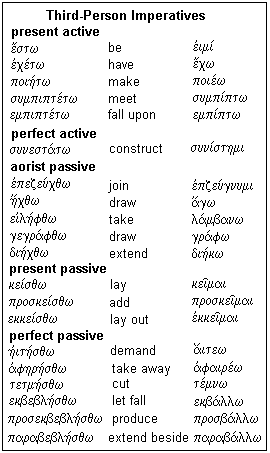
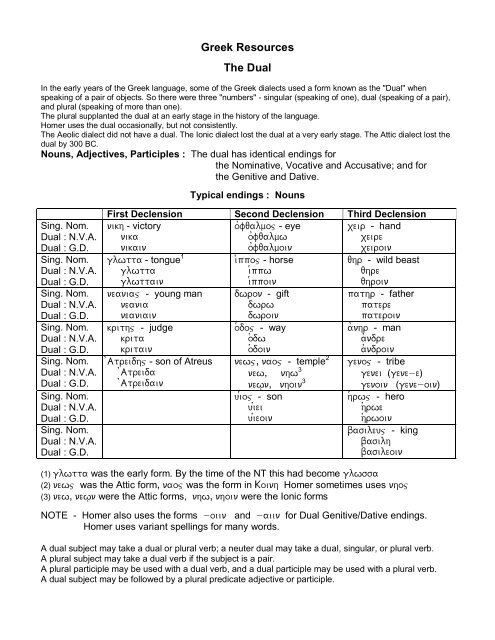
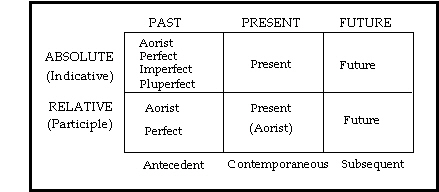
Aorist Imperative Attic

Notice that the plural forms of the aorist active indicative of γινώσκω use a second aorist stem but first aorist endings.
Aorist imperative attic. Abbreviated aor verb forms usually express perfective aspect and refer to past events similar to a preterite. Identify whether it is a first or second aorist and if the latter whether the second aorist is thematic or athematic and 2. Change from the aorist tense to the present and imperfect tenses in the same person and number.
Personal endings of the active imperative. Of αἰρῶ αἰρέω choose. Here chose translates an aorist middle form 2nd aor. For the distinction of time between the present and aorist see 313.
The tenses occurring in the imperative are the present aorist and perfect but only a few perfect active forms occur and these are rare. Aorist ˈ eɪ ə r ɪ s t. Because the aorist stem of γινώσκω γνω ends in the long vowel ω the thematic vowel of the singular endings is lost through contraction. The literary greek of athens in the fifth and fourth centuries bc attic.
The presence of ὑμᾶς you functioning as the direct object means this clause cannot be reflexive. The imperative is used to express a command exhortation or an entreaty.