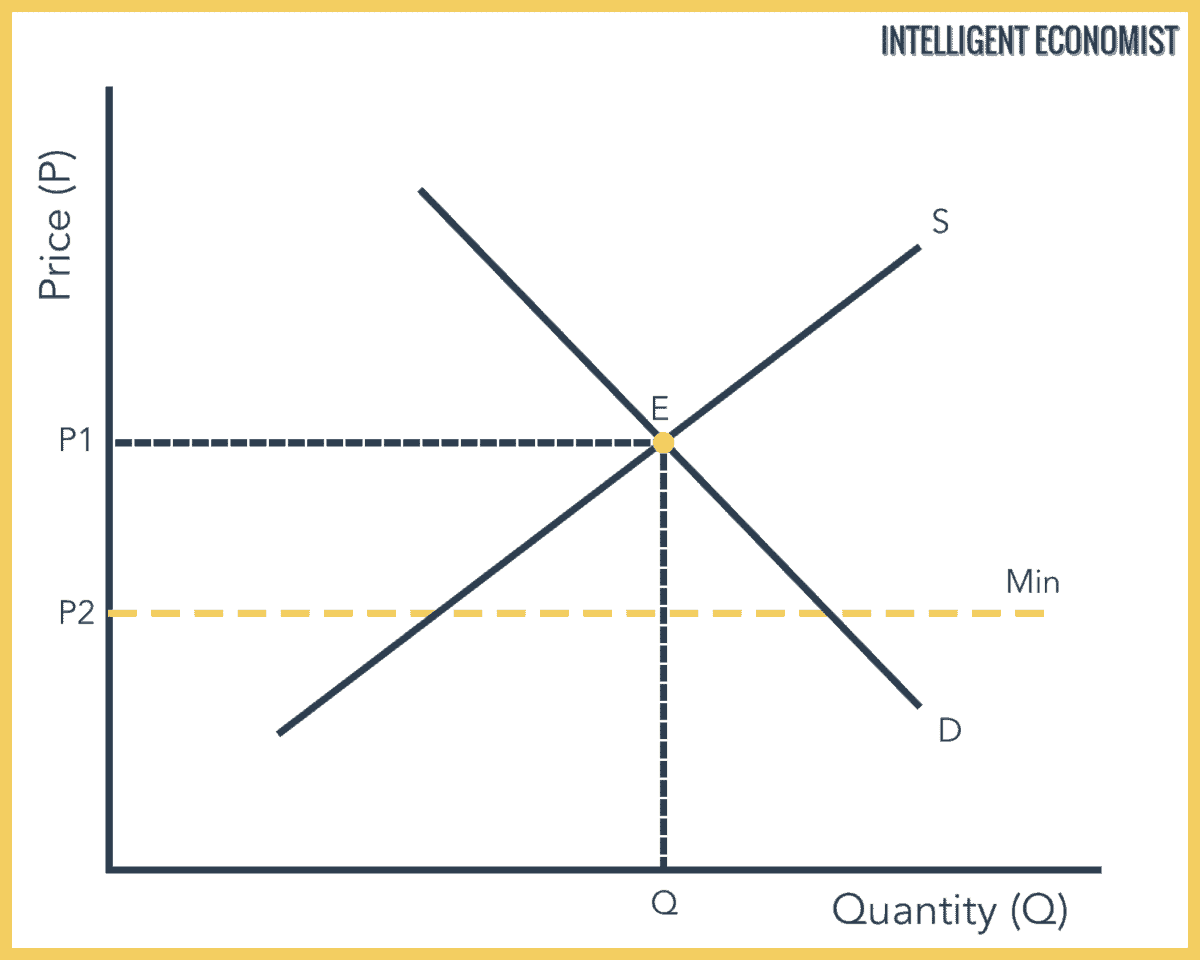
A Price Support Program Using Price Floors

A price support above the equilibrium price leads to a surplus.
A price support program using price floors. A price floor is a minimum price enforced in a market by a government or self imposed by a group. The farm service agency fsa is an organization with a legacy of responding quickly to program legislation being service oriented and focusing on producer needs. Unlike price floors however price supports don t operate by simply mandating a minimum price. Typical examples include minimum wage agricultural support price and price agreed by an oligopoly.
Price supports sets a minimum price just like as before but here the government buys up any excess supply. The ccc buys grain at the support price stores it and releases it back into the market if the market price rises to a prescribed trigger level of say 140 percent of the support price. Farm prices and thus farm incomes fluctuate sometimes widely. The deadweight loss of price supports involves the usual deadweight loss plus the entire cost of unconsumed goods.
Price supports are similar to price floors in that when binding they cause a market to maintain a price above that which would exist in a free market equilibrium. In the case of a price control a price support is the minimum legal price a seller may charge typically placed above equilibrium. In this manner the policy protects growers against the risk of low prices but also protects consumers against unusually high prices. A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
It tends to create a market surplus. Agriculture price supports that establish a price floor at which agricultural products may be 3 purchased that exceeds the market clearing price result in the quantity of these products supplied exceeding the quantity demanded at the floor price. This is even more inefficient and costly for the government and society as a whole than the government directly subsidizing the affected firms. A price support is a combination of two programs.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service. They can set a simple price floor use a price support or set production quotas. The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the equilibrium values of economic variables will not change often described as the. It is the support of certain price levels at or above.
Around the world many countries have passed laws to create agricultural price supports. Instead a government implements a price support by telling producers in an industry that it will buy output from them at a. In economics a price support may be either a subsidy a production quota or a price control each with the intended effect of keeping the market price of a good higher than the competitive equilibrium level.